In the Spring of 2008 I taught Wichita State University’s Assembly Language Programming for Engineers course. As explained in the syllabus, the course used the Z80 microprocessor and the GameBoy platform to introduce general concepts of computer architecture, machine and assembly language programming. Students practiced the ideas and concepts introduced in the course with programming projects on the GameBoy. For their final project students in the course wrote a game. We then held a celebratory public event where kids of all ages could play all the games.
Similar Posts

Avian Migration
In 2018 I collaborated with Artist Lisa Rundstrom and artist/engineer Tom McGuire to create the public art sculpture, Avian Migration at Wichita’s new Advanced Learning Library. Avian Migration consists of more than 1,300 LEDs controlled by 8 motion-activated sensors spread throughout the library. I was primarily responsible for the development and implementation of the software…

SoundBlocks
SoundBlocks is a tangible environment where youth connect blocks to describe network dataflow. The environment explores digital sound manipulation as a personal, meaningful and fun artistic endeavor, rather than as a venture into mathematical, electronic or networking relationships.

Introduction to Audio and Video Synthesis
I taught a course called Introduction to Audio and Video Synthesis which introduced a variety of classic synthesis techniques, digital signal processing, and audio production. Additionally, students were exposed to important class and contemporary electronic works.
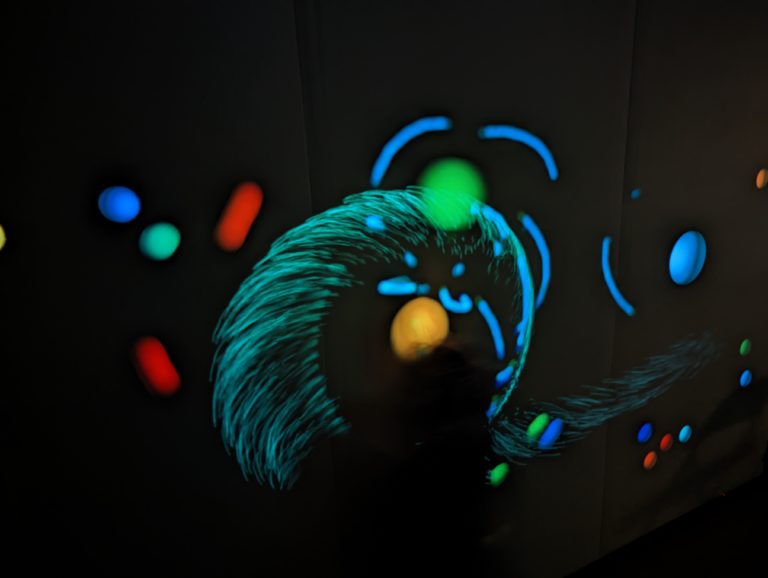

Touch #2
Touch #2 is a playful virtual environment and an interactive, musical instrument. Viewers become participants through play. The work transforms any flat wall into a touch-sensitive surface. A projector and infrared camera mount on the ceiling and infrared emitters mount on top of the wall, allowing the work to detect as many as 10 touches…
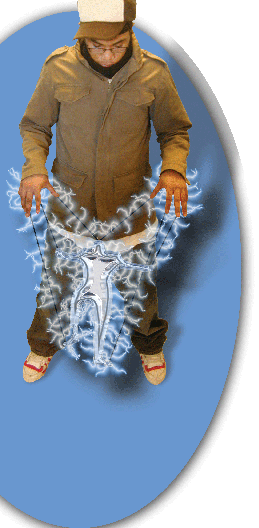
Digital Puppetry
I worked with a team of colleagues, community members, and urban youth. Our intention was to help the youth learn in a playful environment, find personal self-expression, and have their voices heard by communities in Boston. To do this, we adapted commercially available technology to provide a unique medium: digital puppetry.
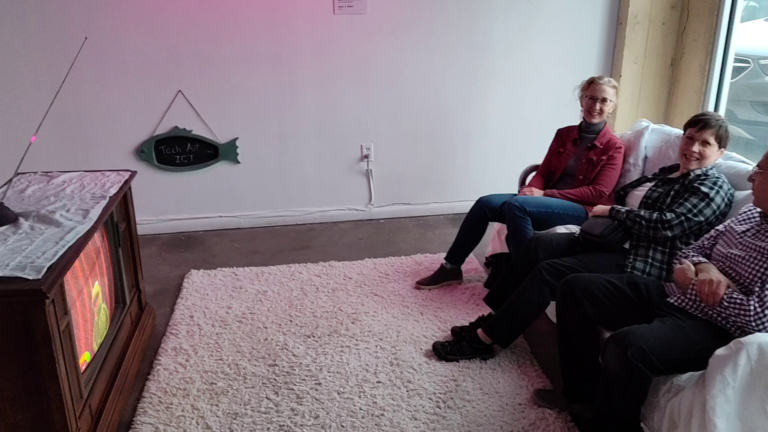

Have a Seat!
Have a Seat! is a playful interactive installation in which a video of a traveler of both time and space urges viewers to sit on a couch. When three people sit close together on the couch a special broadcast or snippet of The Muppet Show plays. Strangers coming to view the work find themselves uncomfortably…