Chord Recognition in Beatles Songs
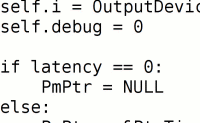
While a graduate student at MIT’s Media Lab, I collaborated with office-mate Victor Adán to explore how if we might train a machine to recognize chord changes in music. We tried multiple models to solve the problem, including Support Vector Machines, Neural Networks, Hidden Markov Models, and a few variations of Maximum Likelihood systems.
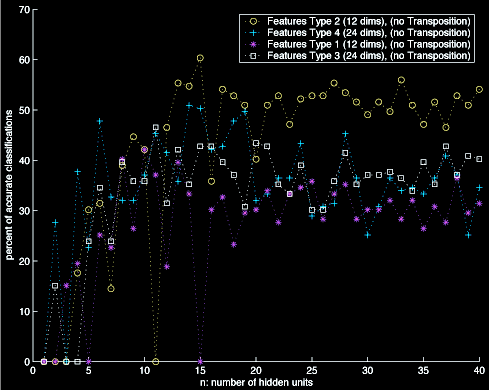
We chose Beatles tunes as a subset of the larger problem and trained our systems with 16 songs from three of their albums. Our systems processed 2700 training samples, 150 validation samples, and 246 testing samples. Our most successful system, a Support Vector Machine, achieved 68% accuracy in testing.
Our intention was to further the research which will lead to applications such as automatic transcription, live tracking for improvisation, and computer-assisted (synthetic) performers. Our models were an extension of the research provided by the following papers:
- Musical Key Extraction from Audio, Steffen Pauws
- Chord Segmentation and Recognition using EM-Trained Hidden Markov Models, Alexander Sheh and Daniel P.W. Ellis
- SmartMusicKIOSK: Music Listening Station with Chorus-Search Function, Masataka Goto
- A Chorus-Section Detecting Method for Musical Audio Signals, Masataka Goto